Cell culture contamination is a major issue for all laboratories as it leads to culture loss. This concern is particularly acute in medical laboratories analyzing very delicate stem cells without antibiotics,
Contamination’s origins?
Contamination is usually due to the presence of microorganism or mycoplasmas.
As for bacteria, literature studies report that the contamination level can reach 5%. This contamination is very difficult to detect: the visual characteristics change suddenly with a muddy development middle or by a color modification.
As for mycoplasmas, their detection by eye is impossible.
They are the smallest independent living organisms and yet the cause of a large number of contaminations.
There are contaminations identified as being of chemical origin: these are non-living products that will have an adverse effect on the cells’ development.
These contaminations are generally due to the medium preparation, including water, whose components or storage conditions may lead to interactions that will prevent the proper development of the culture.
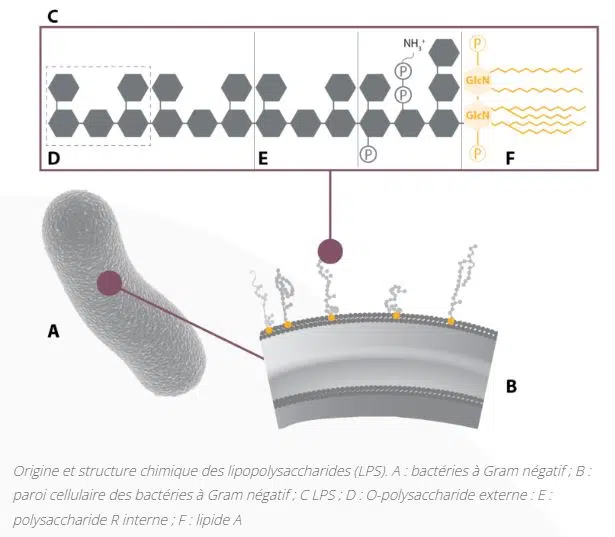
Among these so-called chemical contaminations, those are the endotoxins.
As the name suggests, these are toxins that are found inside….
And more precisely in the outer membrane of some Gram-negative bacteria. These are lipopolysaccharide toxins (LPS) produced by the waste products of gram- bacteria in water.
We also often talk about pyrogen, but do you know what the difference is?
As previously stated, endotoxin is an LPS while pyrogens are polypeptides or polysaccharides that once released cause fever.
https://www.nutrex.eu/fr/articles/les-endotoxines-expliquees/
These chemical or microbial contaminations are often related to non-compliance with prevention processes such as:
- equipment cleaning lacks
- preparation (water, culture media) outside the sterile zone (laminar flow or microbiological safety cabinet)
- a contaminated water bath or bench
- non-disinfected equipment
Contaminations: what impact?
Impacts are important because these contaminations lead to analytical errors but also to a time waste because of the important handling time.
Contamination can reduce productivity, growth rate and cell viability.
This also has a direct financial impact between the time waste and all the reagents, consumables, materials lost.
It is also necessary to note the human impact. Each contamination can come from human or from the good application of the procedures. This leads to a team’s challenging and can also damage the laboratory’s reputation.
How to prevent cell culture contamination?
As for mycoplasmas, there are different tests that can detect them in cultures: specific culture tests, DNA colorimetry tests or PCR detection tests.
However, the best strategies are prevention, early detection and elimination of all infected or potentially infected material.
To reduce the microbiological contamination risk, the handling are carried out in a sterile environment.
Ways to improve processes to reduce the risk of crop contamination include:
- reduce the medium quantities prepared to avoid their degradation by heat or brightness…
- disinfect incubators and other instruments with suitable products
- use equipment whose quality level is compatible with use in cell culture: DNA free, RNase free, DNase free, endotoxins free … –
- ensure the environment cleanliness (dust, spiders can also cause contamination)
- avoid storing cardboard boxes, which are very appreciated by molds as soon as there is a little humidity
Cell culture requires a specific working environment and tools, fortunately, here we know the right partners to accompany you through the whole process, providing you with a coordinated response to contamination risks; so, do not hesitate to complete the form below!